Explain the impact of fabric type and color on the quality and longevity of printed designs.
INTRODUCTION
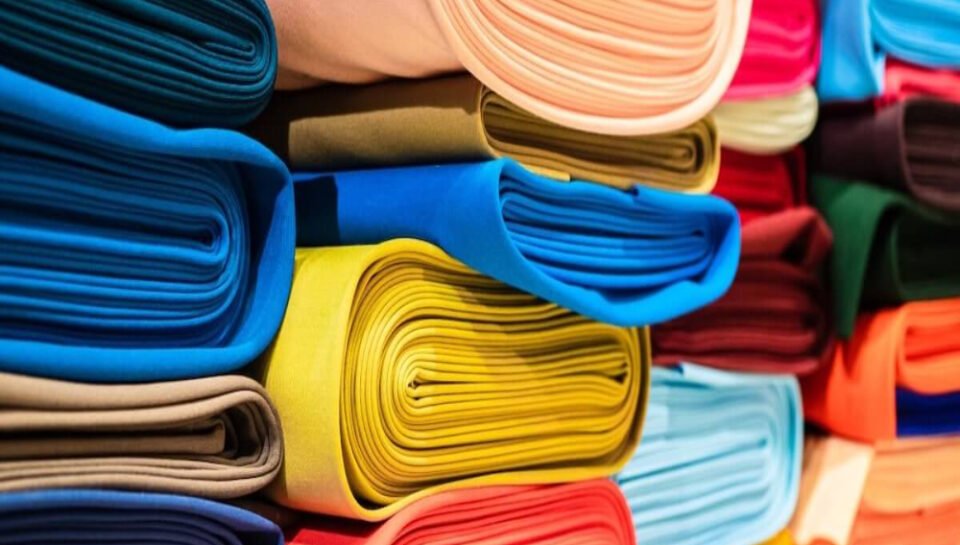
In the world of garment decoration, the type of fabric and its color play a critical role in determining the final look, feel, and durability of printed designs. Whether you’re using screen printing, direct-to-garment (DTG), sublimation, or heat transfer, the textile base affects everything from ink absorption to image sharpness and wear resistance. Understanding how fabric type and color interact with print methods is essential for producing high-quality, long-lasting apparel.
1. FABRIC COMPOSITION AND INK COMPATIBILITY
Different fabrics react differently to various printing techniques.
- Cotton is ideal for screen printing and DTG because it absorbs ink well and holds color vibrantly.
- Polyester is best suited for sublimation, which bonds dye to synthetic fibers.
- Blended fabrics (like cotton-poly) require special care, as they may not react uniformly to heat or ink, potentially affecting print sharpness and longevity.
2. THREAD COUNT AND SURFACE TEXTURE
High thread count and smoother fabrics (like ring-spun cotton) provide a clean surface for crisp, detailed prints. Rougher or ribbed textures can cause ink to settle unevenly, leading to fuzzy edges or color inconsistencies, especially in fine-detail graphics.
3. STRETCHABILITY AND DURABILITY
Elastic fabrics such as spandex or jersey knit may crack or distort printed designs over time if the ink isn’t formulated to stretch. Choosing stretch-compatible inks or flexible printing methods is crucial to maintain the integrity of the design.
4. COLOR OF THE FABRIC AND PRINT VIBRANCY
Fabric color directly influences how colors appear on the final print:
- Light-colored fabrics allow inks to appear true to their intended shades, making them ideal for full-color prints.
- Dark fabrics often require a base layer of white ink (especially in DTG or screen printing) to prevent the design from looking dull or muted, which can add complexity and cost.
- Bright neon or deep-toned fabrics may alter the perception of ink color due to contrast and bleed-through.
5. PRE-TREATMENT AND COLOR FASTNESS
Certain fabrics (particularly dark or synthetic ones) require pre-treatment to enhance ink adhesion and prevent fading. Without proper pre-treatment, prints may peel, crack, or fade prematurely—especially after washing.
6. WASHABILITY AND WEAR RESISTANCE
Fabrics that withstand frequent washing and friction help preserve print quality. Cotton tends to soften and fade with time, while polyester holds up better but can develop pilling. The choice of printing ink and post-print curing also influences how well designs endure repeated use.
7. HEAT SENSITIVITY
Heat-based methods like sublimation or heat transfer may not be suitable for delicate fabrics like silk or low-melt synthetics. Excessive heat can scorch or distort these materials, affecting both the garment and the printed design.
8. ENVIRONMENTAL AND SUSTAINABILITY FACTORS
Natural fabrics such as organic cotton are increasingly preferred for eco-friendly printing. However, sustainability must be balanced with print method compatibility, as not all inks are biodegradable or fabric-safe without additional treatment.
CONCLUSION
The fabric type and color are foundational elements in achieving professional-quality printed apparel. They influence ink absorption, print clarity, color vibrancy, and overall longevity. Choosing the right combination ensures durability, customer satisfaction, and an optimal visual result—making it a critical consideration in any textile printing project.
HASHTAGS
#FabricMatters #TShirtPrinting #PrintQuality #GarmentDesign #InkAndTextile #CottonVsPolyester #DTGPrinting #SublimationTips #TextilePrinting #PrintedApparel #FashionDurability #FabricSelection #DesignLongevity #CustomPrinting #HeatTransferPrinting #ScreenPrintingTips #PrintOnFabric #EcoFriendlyPrinting #TextileDesign #FabricColorImpact #ApparelDesignTips #ColorFastness #WearableDesign #PrintQualityControl #PrintingScience